Gabapentin 600mg vs. 800mg: Breaking Down Side Effects and Efficacy
Gabapentin 600mg versus 800mg in terms of side effects and efficacy, it is essential to consider individual patient needs and response to the medication.
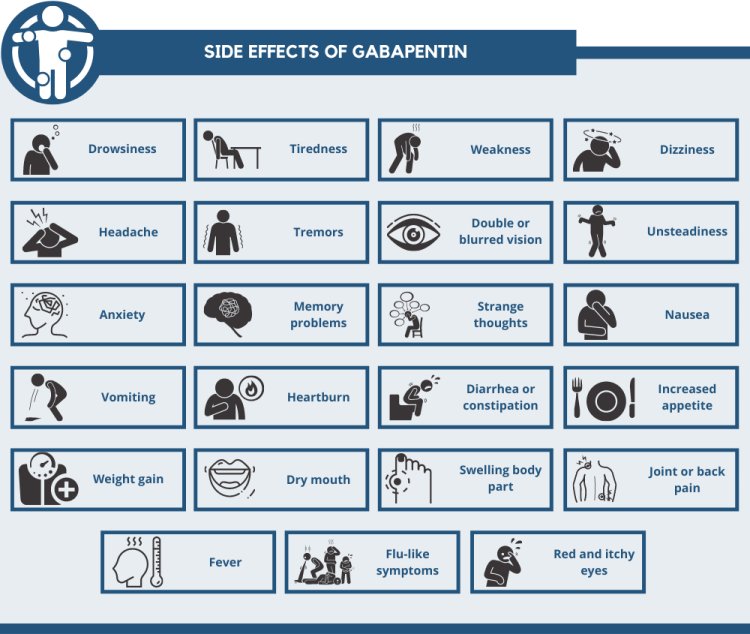
Gabapentin, a widely prescribed medication for neuropathic pain and seizures, is available in various dosages, with 600mg and 800mg being two common options. Understanding the differences in side effects, efficacy, and suitability between these dosages is critical for patients and healthcare providers alike. In this comprehensive guide, we will analyze these differences to provide a clearer picture of which dosage might be more appropriate based on individual needs.
The drug Gabapentin 600mg is frequently given and is well-known for its ability to effectively treat a variety of medical disorders. Nerve discomfort brought on by diseases like fibromyalgia, diabetic neuropathy, and shingles is frequently treated with this dosage of gabapentin.
What is Gabapentin?
Gabapentin 800mg is used with other medications to prevent and control seizures. It also relieves nerve pain following shingles (a painful rash caused by herpes zoster infection) in adults. Gabapentin is known as an anticonvulsant or antiepileptic drug.
Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant and nerve pain medication. It works by altering how nerves communicate pain signals to the brain. It is commonly used for:
- Treating neuropathic pain (e.g., diabetic neuropathy, postherpetic neuralgia)
- Managing partial seizures in epilepsy
- Off-label uses such as migraine prevention, fibromyalgia, and anxiety relief
Gabapentin 600mg vs. 800mg: Key Differences
1. Dosage Strength and Composition
- Gabapentin 600mg: Contains 600 milligrams of active gabapentin per tablet.
- Gabapentin 800mg: Contains 800 milligrams of active gabapentin per tablet, offering a higher dose for more severe symptoms.
2. Use Cases
- Gabapentin 600mg is typically prescribed for moderate neuropathic pain or as an intermediate step in dosage escalation.
- Gabapentin 800mg is reserved for patients with more severe symptoms or when lower doses fail to provide adequate relief.
3. Flexibility in Dosing
Both dosages can be divided or adjusted as needed. However, 600mg tablets offer more flexibility for fine-tuning doses compared to 800mg tablets.
Efficacy: Is a Higher Dose Always Better?
1. Effectiveness for Pain Relief
Clinical studies show that increasing gabapentin dosages can improve pain relief, but this benefit plateaus at a certain point. For most patients:
- 600mg often provides sufficient relief for moderate pain.
- 800mg may be necessary for severe, persistent pain.
2. Seizure Control
For epilepsy management, higher dosages like 800mg are more effective in reducing the frequency of partial seizures. However, individual responses vary.
3. Patient-Specific Factors
The efficacy of gabapentin depends on:
- Body weight and metabolism: Heavier individuals may require higher doses.
- Condition severity: Severe conditions may necessitate 800mg or higher.
- Other medications: Concurrent medications can influence how gabapentin works.
Side Effects: Comparing 600mg and 800mg
1. Common Side Effects
Both dosages share similar side effects, including:
- Drowsiness
- Dizziness
- Fatigue
- Coordination issues
However, 800mg tends to have a higher incidence of these side effects due to the increased dose.
2. Gastrointestinal Effects
- 600mg: Mild nausea and bloating are possible.
- 800mg: Symptoms like constipation or diarrhea are slightly more common.
3. Cognitive Effects
Higher doses such as 800mg are more likely to cause:
- Memory problems
- Confusion
- Difficulty concentrating
4. Risk of Overdose
While both dosages are safe when taken as prescribed, 800mg carries a slightly higher risk of overdose symptoms such as extreme drowsiness, slurred speech, and respiratory issues if misused.
Who Should Use Gabapentin 600mg?
- Patients starting gabapentin therapy
- Those with mild to moderate neuropathic pain
- Individuals sensitive to higher doses or prone to side effects
Advantages of 600mg
- Reduced side effect risk
- Easier dose adjustments
Who Should Use Gabapentin 800mg?
- Patients with severe, unresponsive neuropathic pain
- Individuals requiring higher dosages for seizure control
- Those who have tolerated lower doses without significant side effects
Advantages of 800mg
- Greater efficacy for severe conditions
- Convenience for those needing high doses
Titration and Transitioning Between Dosages
1. Starting Low and Going Slow
Patients typically begin at lower doses (e.g., 300mg) and gradually increase to 600mg or 800mg to minimize side effects.
2. Monitoring During Transition
Regular follow-ups with a healthcare provider are essential to:
- Evaluate efficacy
- Adjust dosages as needed
- Monitor for adverse reactions
Patient Testimonials and Real-World Experiences
- Case 1: A 55-year-old diabetic neuropathy patient reported significant relief at 600mg, but side effects became intolerable at 800mg.
- Case 2: An epilepsy patient found 800mg effective in reducing seizure frequency without severe side effects after a gradual titration.
FAQs About Gabapentin Dosages
1. Can I switch between 600mg and 800mg?
Yes, but only under a doctor’s supervision to ensure safe titration.
2. Are side effects permanent?
Most side effects subside over time or with dosage adjustments.
3. How long does gabapentin take to work?
Relief typically begins within a few days, with maximum benefits seen after 2-3 weeks.
Conclusion
Choosing between gabapentin 600mg and 800mg involves weighing efficacy against potential side effects. While 600mg is ideal for moderate conditions, 800mg can be a game-changer for severe cases. Consultation with a healthcare provider is vital to determine the most suitable dosage based on individual needs and treatment goals.
What's Your Reaction?


















